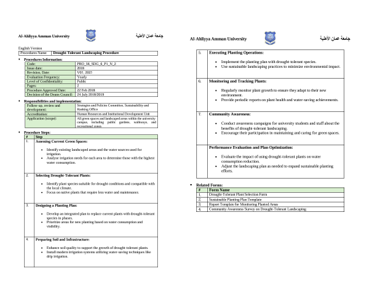
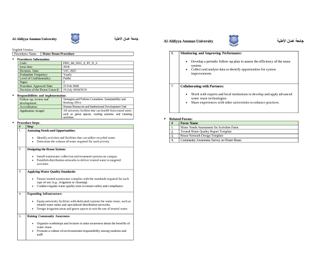
Use of drought-tolerant plants and irrigation designs that reduce water use in campus landscapes.
Water-Smart Landscaping (6.3.5)
Introduction:
Al-Ahliyya Amman University (AAU) has transformed its campus landscape into a model of sustainable water management through the implementation of water-smart landscaping principles. The university’s approach emphasizes the use of drought-tolerant native plants, efficient irrigation systems, and the reuse of treated and harvested water for irrigation purposes.
This initiative is guided by official sustainability documents including:
These frameworks ensure that every green zone on campus follows low-impact, water-efficient, and climate-adapted design standards, directly supporting SDG 6.4 (Water-Use Efficiency) and SDG 15.3 (Land Degradation Neutrality), while contributing to SDG 13 (Climate Action) through resilience-oriented landscaping.
Centers and Departments:
Activities:

01
4. Green Corridor and Eco-Garden Development (2024–2025)
As part of the Water-Smart Campus Master Plan, AAU developed new shaded pathways and eco-gardens connecting faculties.
These areas use drought-tolerant trees, layered vegetation, and natural mulching to maintain moisture.
This design improves aesthetics, biodiversity, and water efficiency simultaneously.
01
5. “Green Campus, Blue Planet” Awareness Campaign (2025)
Organized by the Sustainability and International Ranking Center, this campaign—aligned with the Water Management Education and Awareness Policy educated students and staff on sustainable landscaping and the importance of using native plants.
The campaign promoted community ownership and sustainable environmental behavior.
Impact Evaluation & Development Plan
- Performance Evaluation
- Coverage: 100% of campus green areas follow drought-tolerant landscaping standards.
- Water savings: ~40% reduction in irrigation water use compared to 2022 baseline.
- Reuse efficiency: 100% of irrigation water sourced from treated or harvested systems.
- Biodiversity impact: 25 native plant species maintained and expanded annually.
- Environmental education: >1,000 students engaged in awareness and field projects since 2023.
- Development Actions
Action 1: Expand smart irrigation automation to cover all campus zones.
Action 2: Integrate real-time soil and weather sensors for adaptive irrigation scheduling.
Action 3: Develop research projects on green roofs and vertical gardens using treated water.
Action 4: Collaborate with local municipalities on urban greening and heat island mitigation.
Action 5: Publish an annual Water-Smart Landscaping Performance Report with metrics on reuse, biodiversity, and carbon impact.
- Benchmarking & Best Practice
Adopted Practice: Aligned with FAO’s Guidelines for Efficient Water Use in Arid Landscapes and the Jordanian Ministry of Water and Irrigation’s National Water Strategy (2023–2040).
Local Adaptation: AAU integrates native species selection, natural mulching, and treated-water irrigation systems adapted to Jordan’s semi-arid climate, reducing evaporation and runoff losses.
Future Benchmark Goal (by 2028):
- Achieve an additional 20% reduction in irrigation water use.
- Expand biodiversity coverage to 40 native plant species.
- Develop a carbon-positive landscape zone powered by solar irrigation systems.
Institutional Integration SummaryWater-smart landscaping is a cornerstone of AAU’s Sustainability Action Plan, managed collaboratively by the Sustainability and International Ranking Center, General Supplies Department, and Hourani Center for Applied Scientific Research.
The initiative connects infrastructure, environmental research, and student engagement into one ecosystem of sustainable landscape management.Through this integrated governance model, AAU not only conserves water but also enhances biodiversity, supports environmental education, and demonstrates measurable alignment with SDG 6.4, SDG 13, and SDG 15.
The university’s landscape now serves as a living laboratory for sustainability, reinforcing its role as a national leader in sustainable campus development.